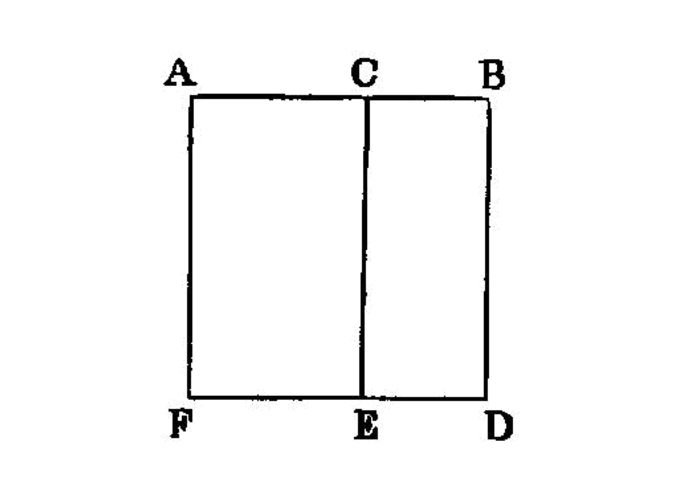Proposition 2.1

If there be two straight lines, and one of them be cut into any number of segments whatever, the rectangle contained by the two straight lines is equal to the rectangles contained by the uncut straight line and each of the segments.